Using an AED
SCA occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating effectively due to an electrical malfunction. Without rapid intervention, SCA is almost fatal. AEDs are designed so that non-medical personnel can safely and effectively use them to save lives.
The information below will provide you with knowledge on everything you may need to know.
What is an AED?
AED stands for Automatic External Defibrillator. It is a portable defibrillator used to administer an electric shock to a person experiencing Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) to restart the heart. AEDs are designed so that an individual with no medical training can safely and effectively use them to save lives. AEDs will provide clear instructions that makes them easy for everyone to use in a stressful environment.
What does AED Stand For?
Automated: Analyzes the heart’s rhythm automatically
External: Pads are applied outside the body
Defibrillator: Delivers a shock to restore normal heart rhythm
AED’s help bridge the crucial gap between collapse and medical help. Remember, every second counts.
How AEDs Save Lives?
An AED helps by:
- Quickly analyzes the patient’s heart rhythm
- Guiding you through CPR and pad placement
- Delivering a shock only when necessary and safely
- Providing time until EMS arrives
AED access can make all the difference in the work. That is why AEDs must be close by and ready to use.
When is an AED Needed?
AEDs is used in case of Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA), when the heart rhythm becomes irregular and chaotic such as ventricular fibrillation and no longer can pump blood effectively.
Signs may look like:
- Sudden Collapse
- No Pulse
- Not Breathing
- Loss of Consciousness
Every minute without defibrillation decreases the chance of survival by 7%–10%. After 10 minutes, survival rates are extremely low.
What is Ventricular Fibrillation (VF)?
VF is the most common abnormal heart rhythm that is found in victims of Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA). It occurs when the electrical system malfunctions, which causes the lower chambers (Ventricles) to quiver instead of in a coordinated rhythm.
Due to that, the heart cannot pump blood effectively into the brain and other important organs. Without immediate treatment, VF rapidly deteriorates into asystole (Flatline) making survival impossible without early intervention very critical.
Learn more about VF
How is Ventricular Fibrillation (VF) Treated?
The only effective treatment for VF is defibrillation which proves a controlled electric shock to the heart which gives the heart a chance to reset and restore in a normal rhythm.
An AED is designed to provide VF victims with defibrillation.
AEDs are designed to:
- Detect life-threatening rhythms automatically
- Guide rescuers with clear voice and visual prompts
- Deliver a shock safety
What is Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA)?
SCA occurs when the heart suddenly stops beating effectively due to an electrical malfunction. The person collapses, becomes unresponsive, stops breathing, and has no pulse. Without rapid intervention, SCA is almost fatal.
Good news: An AED can restore normal rhythm with a life-saving electric shock. The combination of AED and CPR can increase the survival rate of SCA victims by 40%.
Who is at risk of SCA?
Sudden Cardiac Arrest can strike anyone, at any time. Children, Athletes, Teenagers, and Healthy Adults can all suffer from SCA—even those without any prior risk factors. That’s why having an AED Advantage helps you respond confidently and effectively. AEDs should be accessible in public and private settings.
What is the recommended treatment for SCA?
Defibrillation is the only proven method to restore normal heart rhythm in the event of SCA.
How much time do I have to respond?
Only a few minutes.
- If defibrillation is within the first 3 minutes: Survival chance is over 70%
- After 10 minutes: Survival is extremely low
- Safety Rule: Defibrillators should be in a three-minute walk of anyone, anywhere
Is Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) enough?
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) helps maintain blood flow to vital organs through chest compressions and mouth-to-mouth temporarily but does not correct the underlying rhythm. AEDs are essential to deliver the shock and restore the heart to normal activity.
Most CPR training now includes AED use. AED and CPR are the nest combination for survival.
Where AEDs Belong?
Everywhere! Below you will find where AEDs can be commonly found.
Offices and Workplaces: Employee safety and customer safety
Fitness Centre and Sports Facilities: Prepare of physical exertion related incidents
Schools and Community Spaces: Protect large crowds of students, staff and visitors.
Residential Building: Protect those who live in the building
AED Solutions can help you find the right AED to match your location, environment and usage needs.
**Rule: An AED should be within a 3-minute walk of an emergency**
Where should I store an AED?
Visibility and access are key.
- Use a wall-mounted cabinet or bracket (Used Heated Cabinet if outdoors)
- Add clear signage and mark the location on floor plan
- Place in central area where access is easy and fast
How does an AED work?
When someone collapses, the AED guides the user through the rescue process. Below are the following steps:
- Call for Help: Call 911 for emergency services

- Turn the AED On: AED device will have a single button to power on

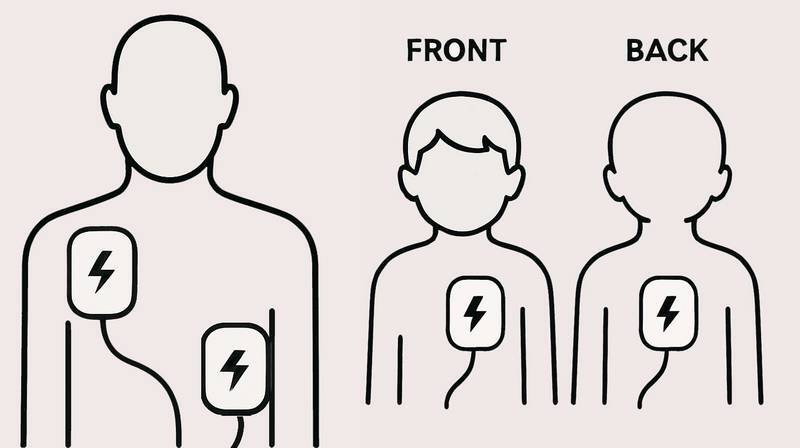
- Attach Pads: Two adhesive pads are placed on the patient’s chest
- Adult: One pad below the right collarbone and the other pads near the left ribcage
- Child or Infant: One pad placed on the middle of chest and other pads on the middle of back
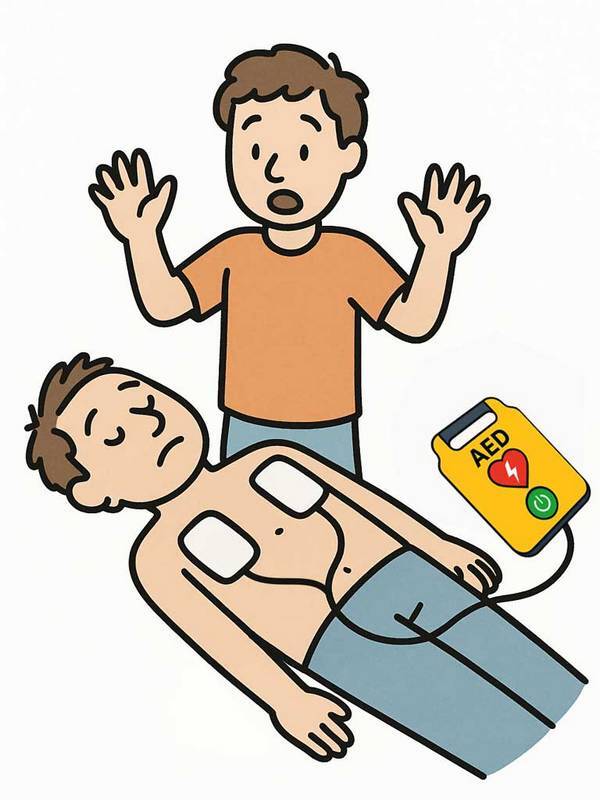
- AED Device Analyzing: Stand back and let the AED aassess the heart rhythm, do not touch the AED or victim
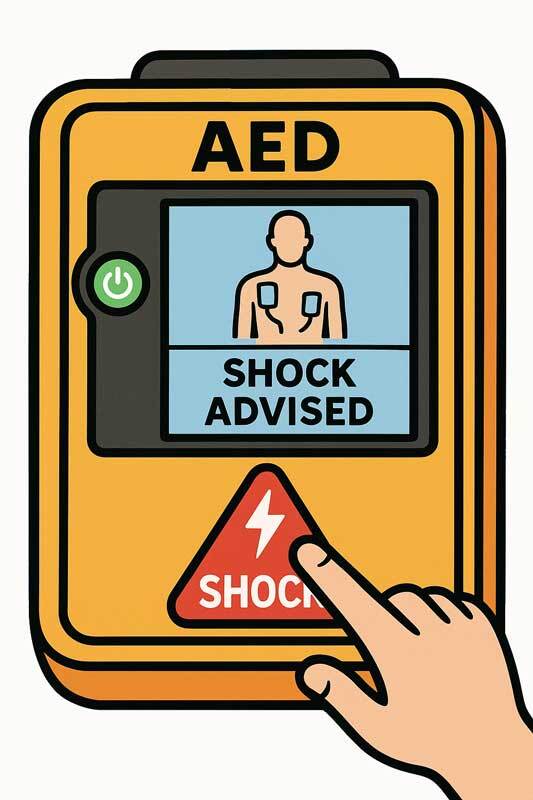
- Shock Advised: If the heart rhythm requires immediate defibrillation, the AED devices will safely deliver a life-saving electrical shock
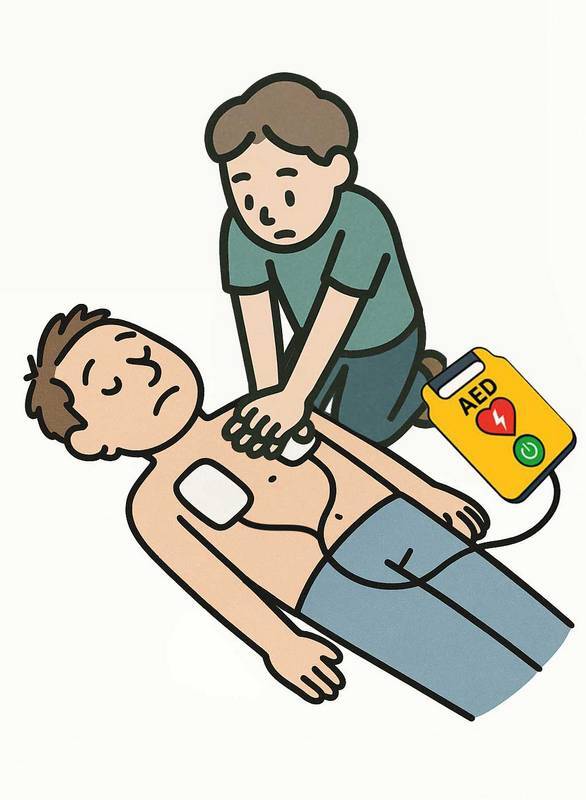
- CPR: Start CPR immediately after the shock. Follow the metronome from the AED (100-120 compressions per minute)
Clear voice prompts and diagrams simplify the process during high stress.
All AEDs will walk you through the process and some AED will provide real-time CPR coaching (for example ZOLL AED 3 and ZOLL AED Plus)
Don’t wait for a crisis to happen and realize you needed one. Act today! Reach out to our team for guidance, product options and support.












